E211 - Sodium Benzoate
 Author: Joe Fowler
Time for reading: ~3
minutes
Last Updated:
January 27, 2026
Author: Joe Fowler
Time for reading: ~3
minutes
Last Updated:
January 27, 2026
CHAPTERS (Table Of Contents)
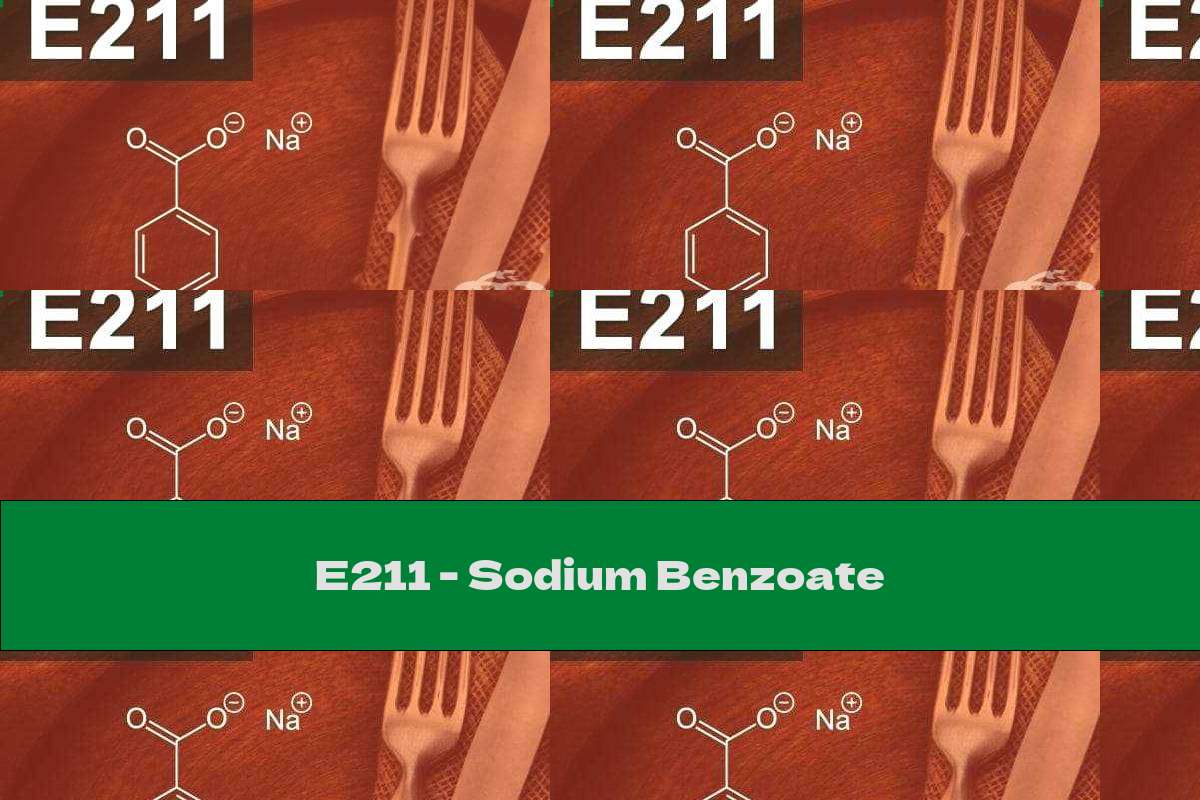
Characteristics: E 211 is a frequently used preservative that guarantees the freshness of the products. Inhibits the development of cells of yeast, fungi and some bacteria. It is found naturally in blueberries
Characteristic
E 211 is a commonly used preservative that guarantees the freshness of the products. Inhibits the development of cells of yeast, fungi and some bacteria. In its natural form it is found in blueberries, raisins and spices (cloves, cinnamon).
Sodium benzoate is a white crystal that has a slight odor of benzoldehyde or none at all, the taste is sweet. The substance dissolves in water.
The antimicrobial action of benzoate is due to the influence of benzoic acid on the enzyme system of microorganisms. There is a suppressive effect on the cells of yeast and mold, reduces the activity of enzymes that carry out the oxidative reaction, restore and divide.
Sodium benzoate is resistant to boiling, the melting point is 300 ° C. To increase its effectiveness, the pH of the acidic medium should be from 3.8 to 4.5.
Use
In the food industry it is used as a preservative for fatty foods, mayonnaise, fruit products, meat, fish, beverages, purees; It is also found in: sauces, caviar, fruit cakes, pickled cucumbers and olives, shrimp, pineapple juice, canned food, spices.
Sodium benzoate is used as an antiseptic and fungicide in a weakly acidic environment. Helps to improve the taste of fresh products. The moment of processing with the preservative is regulated by the technological process of production. Sodium benzoate is pre-dissolved in water (50 g of benzoate in 100 ml of water), the resulting solution is added to the product.
It should be noted that only one type of food supplement is rarely used in modern production. Thus, when benzoate is co-administered with lactic acid, these substances complement each other's preservative properties; the combination of sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate gives a synergistic effect, ie the inhibition of lactic acid bacteria is stronger than with each salt individually.
Typically, E211 is used in combination with colorants and stabilizers. Its content in soft drinks with orange color reaches 25 mcg per 250 ml. Sodium benzoate should not be used in conjunction with vitamin C, because then, as a result of oxidation, especially at high temperatures and strong light, benzene is formed, which is a carcinogen.
Benzene damages the DNA structure, which is the cause of serious diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, cirrhosis of the liver and others.
The increased formation of benzene is influenced by factors such as: the presence of benzoic acid in the presence of ascorbic and benzoic acids, the storage of soft drinks in a warm place. This process can be prevented if sugar or calcium disodium salt EDTA is added to the drinks.
Sodium benzoate is used to protect various types of tobacco from mold. Due to its antiseptic properties, the substance is used in pharmaceuticals (as an expectorant in cough syrups). In the chemical industry it is used in the production of adhesives, dyes, polymer stabilizers; in the aviation industry: protects galvanic coatings and aluminum elements.
Impact on humans
Sodium benzoate is approved in most countries for canning many foods. Its maximum permissible amount is from 0.15 to 0.25%, and the daily consumption should not exceed 5 mg / kg. Adverse effects on the body are expressed in the provocation of allergic reactions and the development of cancer. Avoid contact with respiratory system and eyes.
Benzene enters the body not only through food. We inhale up to 220 mcg of it daily, and the reason is polluted air. Smoking is also a source of the substance.
Preservative is banned in some countries. It is on the list of permitted additives in Europe, but a substitute is being sought because E 211 adversely affects children's behavior and mental development.
- E219 Sodium methyl p-hydroxy benzoate
- E217 Sodium propyl p-hydroxy benzoate
- E215 Sodium ethyl p-hydroxy benzoate
- E218 Methyl p-hydroxy benzoate
Related Articles
- The Role of Sodium Methyl Para-Hydroxybenzoate in Nutrition: Preservative Properties & Health Concerns
- The Role of Sodium Methylparaben in Nutrition: Uses, Controversy, and Safety
- The Ultimate Guide to Disodium Diphosphate in Nutrition
- The Nutritional Value of Potato Chips: Calories, Fat, and Sodium Content
- Propylene Glycol Dibenzoate: Uses, Health Effects, and Alternatives in Food Industry