E316 - Sodium Erythorbate
 Author: Leticia Celentano
Time for reading: ~1
minutes
Last Updated:
January 27, 2026
Author: Leticia Celentano
Time for reading: ~1
minutes
Last Updated:
January 27, 2026
CHAPTERS (Table Of Contents)
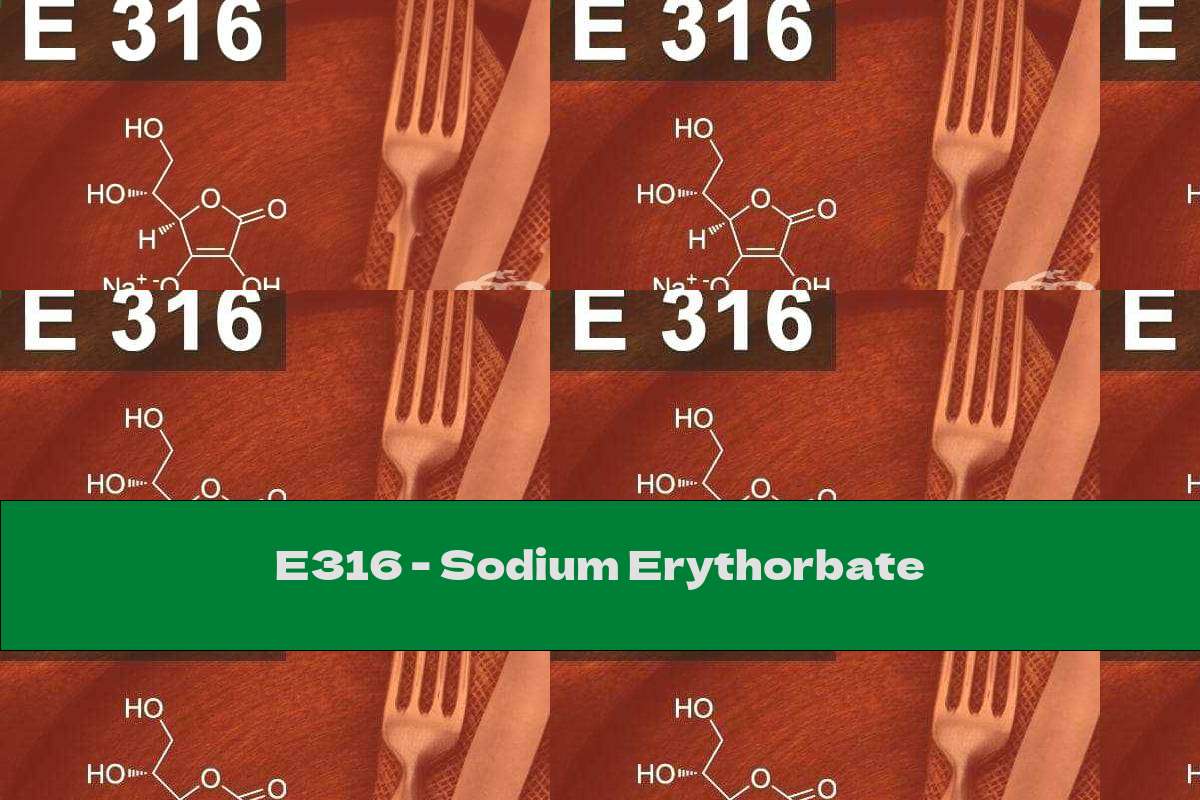
Characteristics: Food supplement E 316 (sodium erythorbate or sodium iso ascorbate - Sodium erythorbate or Sodium isoascorbate) is an antioxidant, which is the sodium salt of ascorbic acid. Etc
Characteristic
Food supplement E 316 (sodium erythorbate or sodium isoascorbate - Sodium erythorbate or Sodium isoascorbate) is an antioxidant that is the sodium salt of ascorbic acid. It is a white crystalline powder or odorless granules, the taste is slightly salty. The solubility in water and alcohols is good, in glycols - medium, and in fats and oils the substance is practically insoluble. It is characterized by antioxidant properties typical of ascorbic acid salts. Sodium erythorbate should be stored in containers that do not allow moisture or light to enter because it reacts easily with water and oxygen. It is obtained by the interaction of ascorbic acid with sodium hydroxide, also from plants such as: sugar beet, corn, sugar cane, in the extraction of sugar from them.
Use
The food additive E 316 is widely used in the food industry as an antioxidant, ie it slows down the oxidative processes in food products. It is also used as a color stabilizer and acidity regulator. It is added in the production of sausages and meat semi-finished products, canned fish; prolongs the shelf life of fruits and vegetables, preventing their darkening, ie oxidation by oxygen in the air.
Sodium erythorbate is used in the manufacture of confectionery, fats of various origins, alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages, in bakery. In the chemical industry it is used to stabilize and prevent oxidation in enzymatic and galvanic processes.
Impact on humans
The permissible daily dose of E 316 is 5 mg / kg body weight. The additive is authorized in EU countries and is considered safe for use in food. Sodium erythorbate has a low vitamin activity (about 5%) compared to sodium ascorbate, so it is not used as a vitamin. It is easily oxidized in the body and excreted quickly from it, this is the reason why its participation in the oxidation-reduction processes is insignificant.
Research is currently being conducted on the mutagenic and teratogenic effects of the substance on the human body.
- E211 Sodium benzoate
- E223 Sodium metabisulfite
- E250 Sodium nitrite
- E262 Sodium acetate, Sodium diacetate
Related Articles
- The Role of Sodium Methyl Para-Hydroxybenzoate in Nutrition: Preservative Properties & Health Concerns
- The Role of Sodium Methylparaben in Nutrition: Uses, Controversy, and Safety
- The Ultimate Guide to Disodium Diphosphate in Nutrition
- The Nutritional Value of Potato Chips: Calories, Fat, and Sodium Content
- The Role of Sodium Tripolyphosphate in Nutrition: Uses and Considerations