E493 - Sorbitan Monolaurate
 Author: Karen Lennox
Time for reading: ~1
minutes
Last Updated:
January 27, 2026
Author: Karen Lennox
Time for reading: ~1
minutes
Last Updated:
January 27, 2026
CHAPTERS (Table Of Contents)
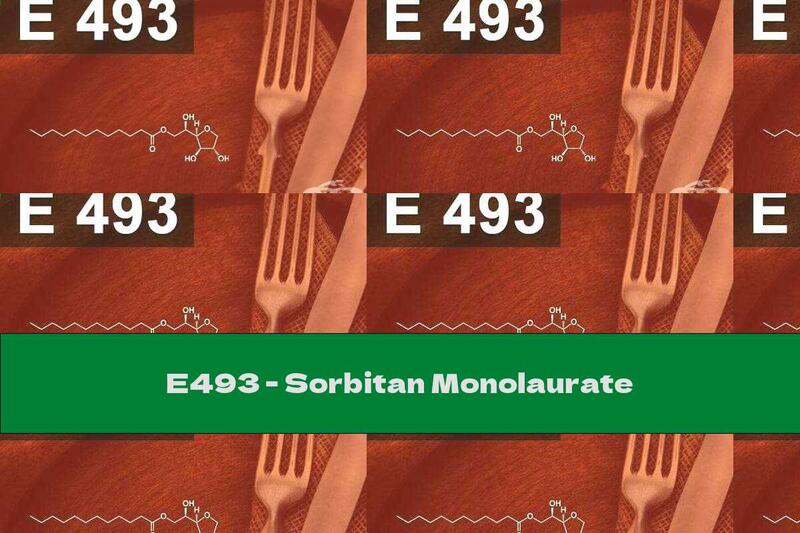
Characteristics: Sorbitan monolaurate is a combination of partial esters of sorbitol and its mono- and dianhydrides with lauric acid. The substance has a thick waxy consistency or is p
Characteristic
Sorbitan monolaurate is a combination of partial esters of sorbitol and its mono- and dianhydrides with lauric acid. The substance has a thick waxy consistency or is a powder with a creamy to yellow-brown color. The additive dissolves well in alcohol, liquid hydrocarbons, forms a dispersion in warm water, is practically insoluble in cold water. E 493 is obtained by esterification of sorbitan with oleic acid with the simultaneous formation of anhydride. The pure substance often contains impurities in the form of free sorbitans and free fatty acids.
Use
The food additive E 493 is used as a stabilizer, thickener and texturizer in the production of concentrates for soft drinks, fruit decoctions and teas in a certain amount; also in the preparation of milk and cream substitutes, confectionery, chewing gum, sauces, fillings. Along with other sorbitans, the substance is added to baker's yeast and biologically active additives, and is also used as a glazing agent for fruits.
Outside the food industry, the additive is used as a stabilizer and emulsifier in the production of cosmetics (creams, lotions, deodorants), drugs and emulsions for plant treatment against pests.
Impact on humans
The allowable daily dose is about 25 mg / kg body weight. In the human body, sorbitan monolaurate breaks down into sorbitol and lauric acid, which in turn are completely absorbed. In some European countries (eg Germany) the additive is banned. They are based on the fact that the substance has not been studied well enough and not all laboratory tests have been completed.
Exceeding the specified daily dose may irritate the lining of the digestive tract, which carries a risk of disease.
- E491 Sorbitan monostearate
- E492 Sorbitan tristearate
- E494 Sorbitan monooleate
- E495 Sorbitan monopalmitate